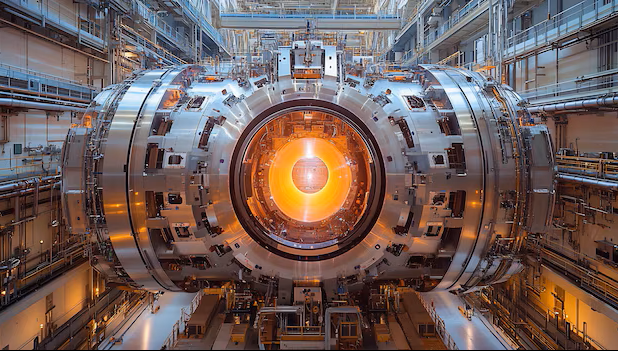
The Race to Net-Positive Power and a Trillion-Dollar Market
The dream of recreating the Sun’s power on Earth is no longer a distant fantasy. In 2025, fusion energy is having its renaissance — with breakthroughs from the US to China and AI reshaping reactor design. From private startups to scientific giants, the race to achieve sustainable fusion is intensifying.
Here’s how the latest global efforts are redefining the clean energy frontier.
AI: The New Architect of Fusion Reactors
Artificial intelligence is emerging as a critical catalyst for accelerating fusion breakthroughs. The partnership between Google DeepMind and leading fusion startups marks a major shift in how research is done — not just faster, but smarter.
DeepMind’s AI systems analyze complex plasma behavior and adjust in real time, helping reactors maintain stability — a notoriously difficult challenge in fusion physics.
This means reactor designs can evolve algorithmically, shortening decades of trial-and-error into mere years of learning cycles.
Startups like UnionRayo in the US are using similar AI-driven systems to fine-tune their plasma confinement processes, edging closer to the holy grail: net energy gain — producing more energy than the reaction consumes.
Together, these efforts prove one thing: fusion’s future isn’t just in physics labs — it’s in neural networks.
Collaboration and the Path to Grid Power
Fusion energy has quietly become the new space race. Governments and corporations are pouring resources into capturing the ultimate clean energy source.
China, for instance, is making headlines with its ambitious plan to be the first to achieve a commercially viable fusion reactor. Its superconducting magnet systems and high-performance tokamaks are redefining what’s possible in plasma control.
Meanwhile, international collaboration remains essential:
General Atomics (GA), for example, is a key player managing the DIII-D National Fusion Facility. By focusing on understanding and managing the behavior of fusion’s hottest particles, GA's efforts are essential in making sustained fusion reactions feasible. Their main roles are:
Operational Milestones: The DIII-D facility recently surpassed its 200,000th experimental cycle (or "shots"), providing invaluable data to the global research community.
Facility Upgrade: A major 2024 facility upgrade enhanced systems for plasma control and diagnostics, aiming to close the key gaps between current experiments and the first pilot power plants (FPPs).
Private Capital vs. Global Ambition
Unlike the early days of nuclear research, today’s fusion ecosystem is fueled by private investment and entrepreneurial boldness.
Companies like UnionRayo and Commonwealth Fusion Systems are drawing in billions from climate-focused investors and tech giants.
Their rapid prototyping and risk-tolerant culture stand in contrast to traditional government-led programs, allowing more agility and innovation.
AI partnerships (like DeepMind’s) further amplify these efforts, blending deep tech and energy science in a way that’s never been done before.
The result? A new generation of fusion startups that operate like Silicon Valley tech labs — but with the power output of a star.
The transition from purely government-funded science to a market-driven industry is marked by a massive infusion of private funding and an intensified geopolitical race. The competition is driving innovation faster than ever, signaling a maturing market ready for large-scale investment.
Investment & Market Indicators:
Total Private Funding: Private fusion companies have raised over $7.1 Billion globally, signaling strong and growing investor confidence in the commercialization timeline.
Talent and Growth: The private fusion sector is rapidly scaling, now employing over 4,100 people worldwide—a 34% increase in just one year.
US Leadership in Startups: The United States leads the commercial sector, hosting 25 of the 45 private fusion companies surveyed in 2024.
The U.S. Fusion Roadmap Takes Shape
In a defining move, the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) unveiled its Fusion Energy Strategy Roadmap, laying the foundation for commercial fusion deployment by the 2030s.
This roadmap transforms fusion from an open-ended experiment into a structured national mission. It identifies six critical challenge areas that will guide development:
Fusion materials and radiation damage
Plasma-facing components and confinement systems
Tritium and fuel cycle management
Blanket systems for energy capture
Full system integration
Advanced confinement and reactor design
Key milestones:
Within the next 2–3 years, national labs will design new fusion test facilities.
By the early 2030s, demonstration reactors could begin generating electricity for the grid.
This roadmap provides the missing bridge between science and scale — aligning academia, industry, and investors around a shared commercial horizon. It complements the rapid strides made by startups and AI innovators, ensuring that breakthroughs translate into infrastructure.
Dream to Deployment
The convergence of AI, private capital, and international collaboration signals a pivotal shift. We’re no longer asking if fusion will happen — but when and where it will ignite first.
Progress may still require patience, but the signs are undeniable:
AI-optimized plasma control is reducing design cycles dramatically.
Cross-border research collaborations are breaking historical barriers.
Private-sector dynamism is turning theoretical physics into real engineering.
Fusion energy has crossed from possibility into inevitability — the only question is which torchbearer will light the world first.
Towards a Fusion-Powered World
The fusion energy landscape is evolving rapidly. The theme that emerges is one of collaboration and convergence. From AI advancements to international research teams and private sector innovation, fusion energy is being shaped by a network of stakeholders all working towards a common goal: a cleaner, more sustainable world. What was once considered a far-off dream is now within our reach, and with the pace of progress, it may soon become a key player in solving the world’s energy crisis, positioning the early movers to dominate a potentially trillion-dollar clean energy market.